



Types of Plating
Plating is a type of surface treatment.
There are several types of plating, depending on the method used.
In this chapter, we will learn about plating’s position
in surface treatment and about the different plating methods.
What different types of surface treatments are there?
The various objects around us will have undergone some kind of surface treatment. Plating is one of the main methods of such surface treatment. The video and diagram below provide a broad summary of the types and characteristics of different surface treatments.

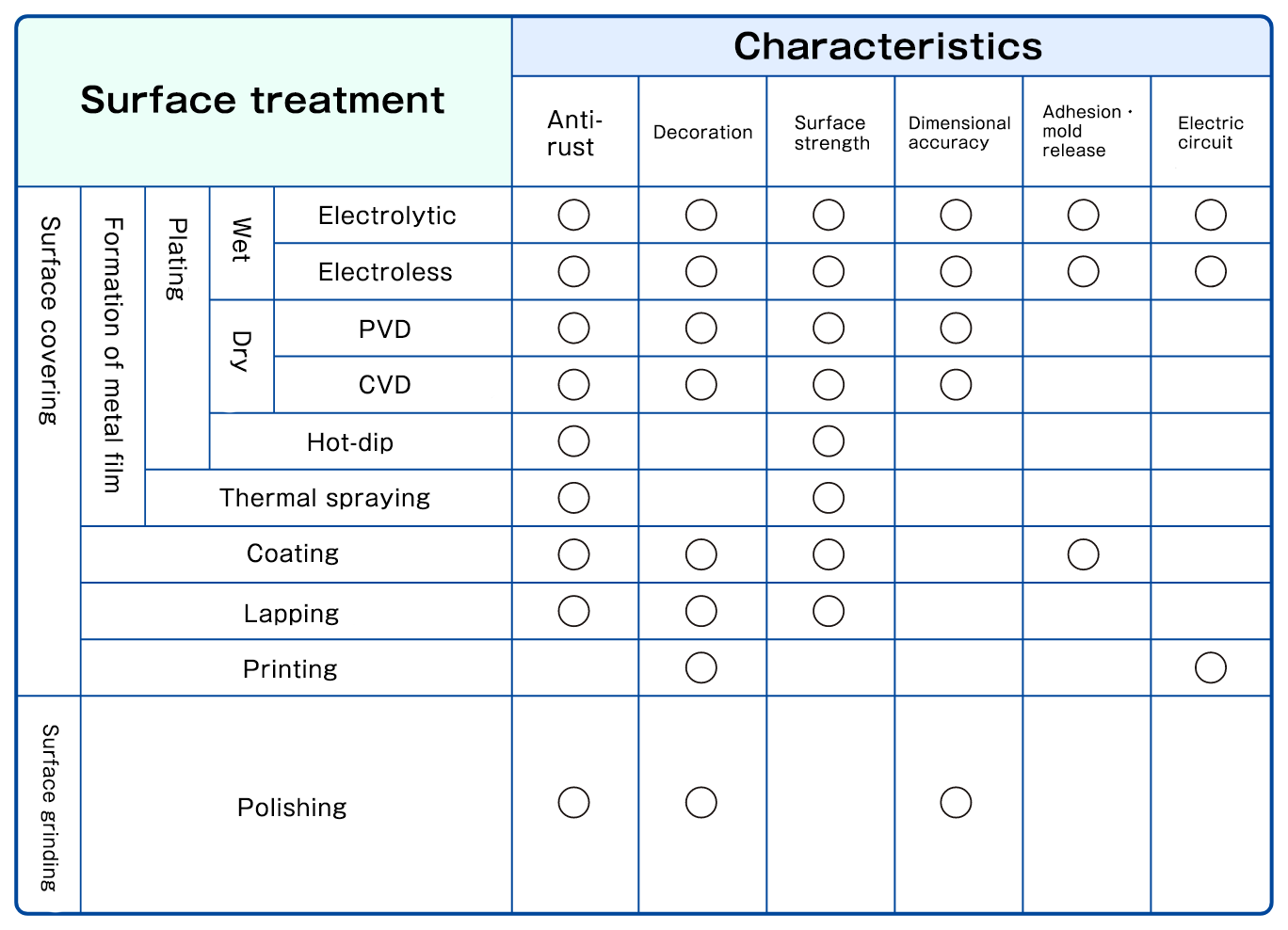
The hot dipping method, a type of plating, is generally called “hot-dip galvanization.” Zinc plating is typical and frequently used for the purpose of rust prevention of large metal products, and inexpensive.
Thermal spraying like plating, is a process for creating a metal coating film on a surface. Thermal spraying forms a metal coating film by spraying metals melted at high temperature onto the substance.
Processes for coating non-metalic materials on the surface include coating, lapping, printing, and others.
Polishing is a method of surface treatment which is not coating, but a process of material removal by scraping.
The advantage of wet plating over other surface treatments is that it imparts numerous functional properties on all manners of materials. We will learn about the functions of plating in Chapter 3.
Another advantage is that it allows easier control of the film thickness.
Dry plating has the disadvantage in obtaining a thick film, while in hot-dip plating, it is difficult to obtain a thin film. With electrolytic plating, however, the thickness of the film can be freely adjusted by controlling the current density and time. With electroless plating, adjusting time and temperature achieve the same result.

What different types of plating methods are there?
There are numerous different methods of plating. The plating method used varies according to the application and required functions, such as the materials to be plated or where the plating is to be applied.
Plating methods can be broadly divided into two categories: wet-plating processes and dry-plating processes. Wet-plating processes use a chemical solution (plating solution) to form a metallic film, while dry-plating processes form a metallic film without any use of chemicals.

What are wet-plating processes?
In wet-plating, the object to be plated is placed in a plating solution that contains metallic components, and a metallic film is formed on its surface.
The methods employed are electrolytic (electroplating) and electroless (chemical) plating.

Electrolytic plating (Electroplating)
Electrolytic plating is a method of plating that uses electrolysis. When an electric current pass through the plating solution, positively-charged metal ions from the anode (or in the solution) are attracted to the negatively-charged object to be plated, where they form a metallic film on the surface.
Electrolytic plating costs less than electroless plating, and plating can be achieved in a shorter time.
Electroless plating (Chemical plating)
Electroless (chemical) plating uses chemical reactions to achieve plating, through either displacement plating or autocatalytic plating.
In this method, a chemical reaction generates electrons on the surface of the object to be plated. Metal ions are attracted to those electrons, causing a metallic film to form.
The advantage of this method is that a uniform film can be created even on materials with complex shapes.

What are dry-plating processes?
In dry-plating, instead of using a plating solution, vaporized metal is used to form a metallic film on the surface of the object to be plated. There are two methods: physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).

PVD(Physical Vapor Deposition)
PVD involves evaporating metal in a vacuum and making it adhere to the object to be plated. This is achieved through vacuum deposition, ion plating, or sputtering.
CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)
In CVD, the object is placed inside a gas containing vaporized metal and heated. This causes a thermochemical reaction that causes a metallic film to form.

In this chapter, we have learned about plating’s position in surface treatment and about different plating methods. When considering what surface treatment to employ, it is essential to understand the characteristics of each treatment before selecting the most appropriate method. In the following chapters, we will learn in more specific detail about how wet-plating is used.

