


Plating of Power Semiconductors
As hybrid vehicles (HVs), which combine engine and motor, and electric vehicles (EVs), which run solely by a motor,
have started to become more popular, electric control has become indispensable in automobiles.
The use of a large-capacity battery to control a high-output motor requires many special devices.
Plating technology is used on these electrical control devices. In this chapter,
we will learn about the plating technologies used on power semiconductors,
which handle high voltages and large electric currents.
What is a power semiconductor?
A power semiconductor, also known as a power device, is a device that controls or converts electric power in products such as industrial machinery, electric vehicles, and home appliances. In addition to their role as a switch to turn voltage and electric current on and off, power semiconductors convert alternating current to direct current, as well as transforming (step-up or step-down) direct current voltage. In recent years, amid the calls for decarbonization initiatives, demand for power semiconductors has increased even further, given their ability to improve energy efficiency.
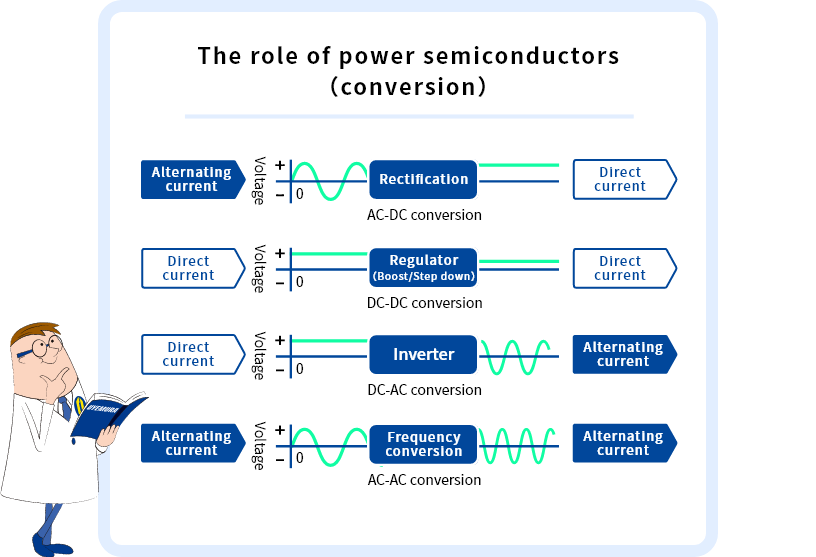
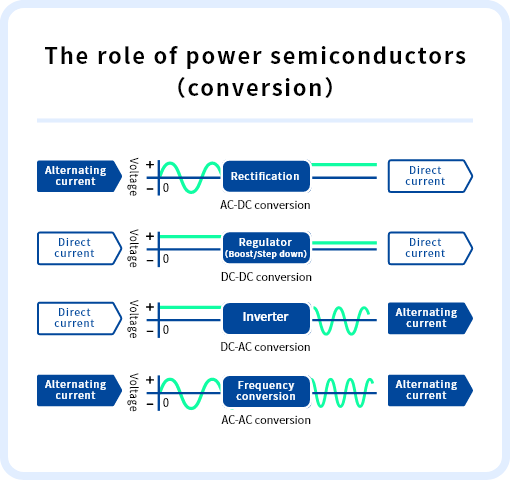
Because the current flow through power semiconductors is an order of magnitude larger than other semiconductor devices, their construction and manufacturing methods differ greatly from regular semiconductors. In addition, because they handle large amounts of power, they generate heat and tend to become very hot. Power semiconductors are designed in such a way as to reduce the power loss of the power semiconductors themselves, which is the cause of heat generation, and to release that heat into the external environment efficiently.
What is an IGBT?
An insulated gate bipolar transistor, or IGBT, is a device whose structure has been designed to make it possible to use power semiconductors even at high voltages and large currents. There are two types of power semiconductor: MOSFET, which are voltage-driven and can operate at high speed, and bipolar, which have low power loss even at high voltage. IGBTs are constructed to incorporate the best features of both these types.
What is a SiC power semiconductor?
Although silicon has been the predominant material used for conventional semiconductors, silicon carbide (SiC), a compound of silicon and carbon, can be used to achieve power semiconductors with lower power loss even at higher voltage. SiC also assists with the minimization and weight reduction of equipment. This has resulted in its growing adoption in electric vehicles in particular, where those benefits are especially great.

What plating technology is used on power semiconductors?
Power semiconductors installed in electric vehicles are incorporated in devices known as power control units (PCU), which control voltage and current.
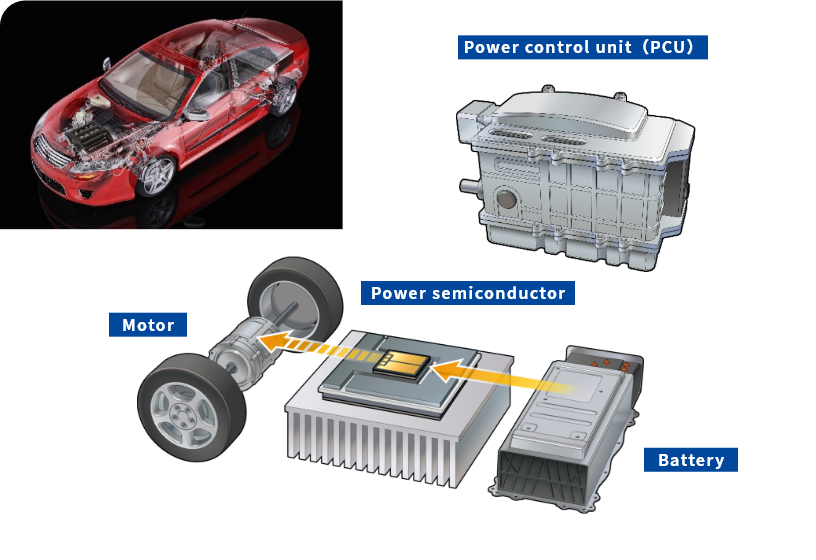
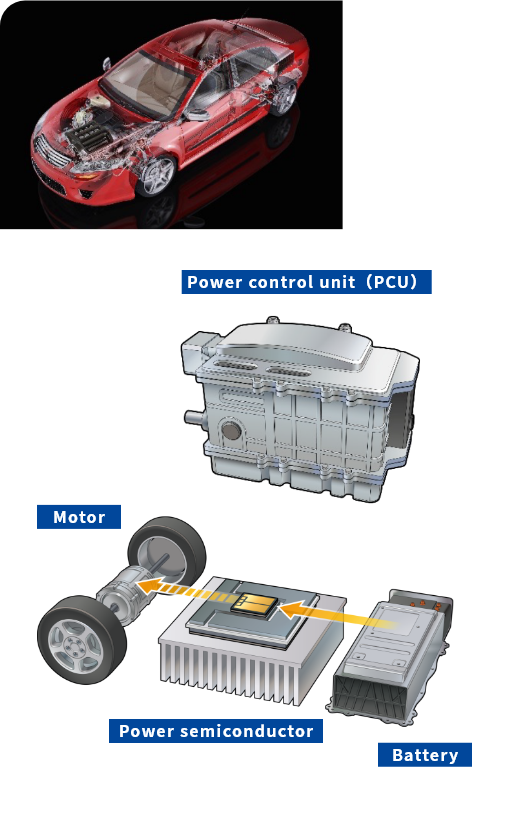
Conventionally, aluminum wire was mounted on aluminum electrodes, but these days, surface-mounted solder bonds are used to increase heat dissipation. To ensure the reliability of the aluminum wire and solder bonds, electroless nickel/gold plating (ENIG) or electroless nickel/palladium/gold plating (ENEPIG) is needed. With the increasingly high voltages and large currents accommodated by power semiconductors, sintered materials (silver and copper) have been proposed as bonding materials that are capable of operation even in such high-temperature environments. Plating films that offer high bonding reliability on sintered materials are now being developed.
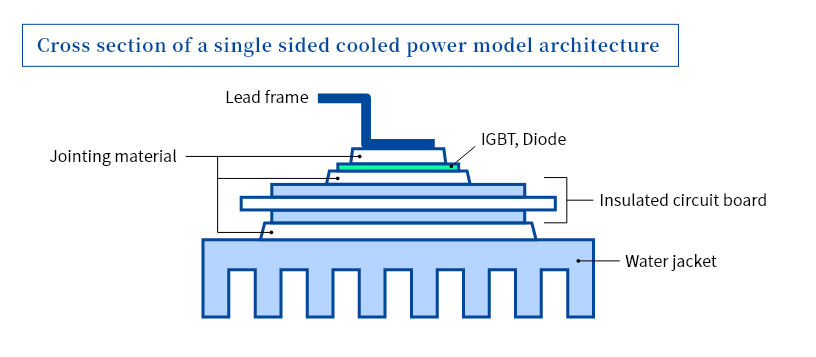

While there are expectations for the increasing adoption of SiC power semiconductors we have learned about in this chapter, particularly for electric vehicles, the largest obstacle is the high cost of their materials and manufacture. In this respect, plating requires a smaller capital investment than dry processes, and it also offers cost advantages because it allows continuous processing, making it suitable for mass production. Plating not only contributes to the improvement of the heat resistance, durability, and heat dissipation of power semiconductors, but it can also assist with productivity and cost gains.

