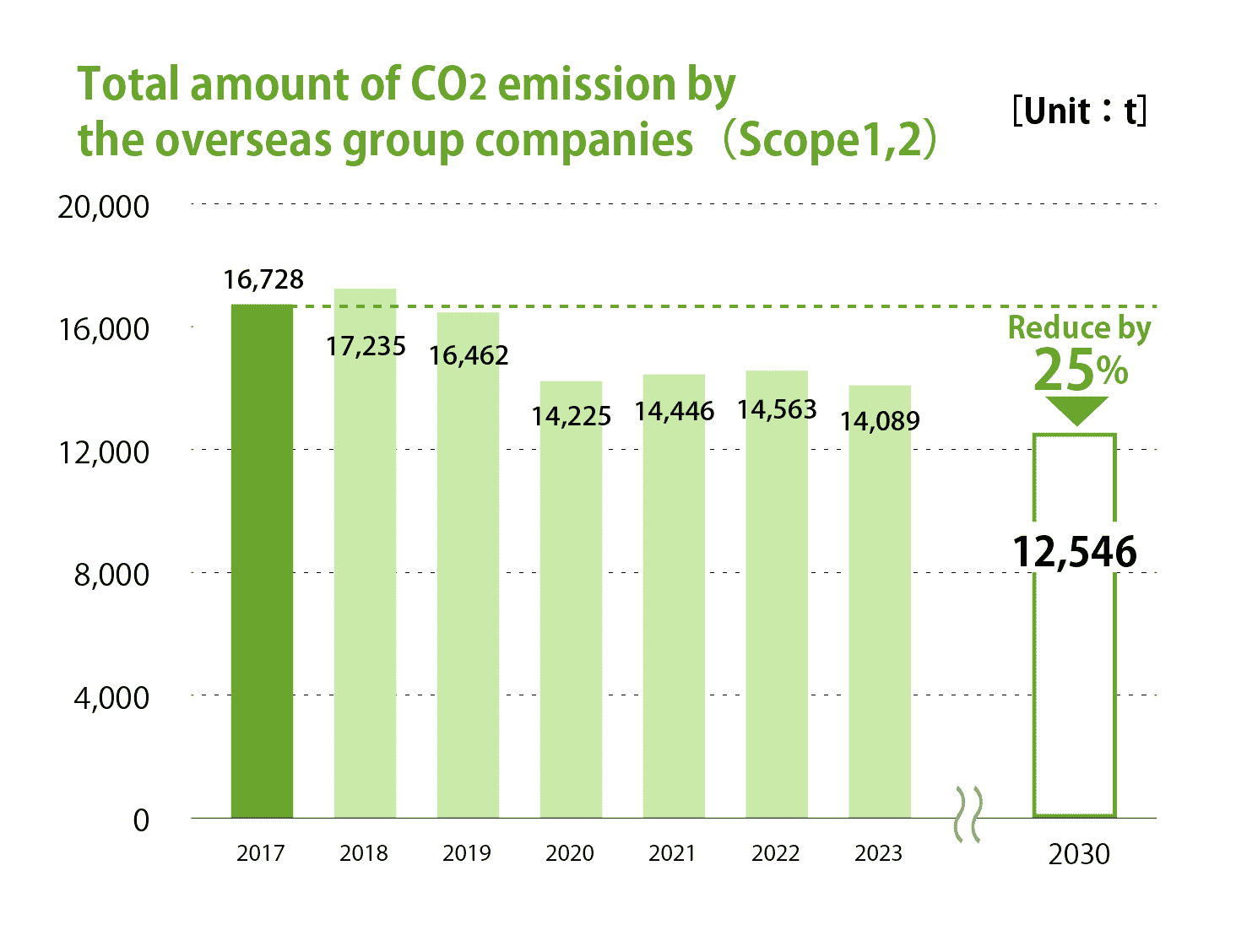The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB), an international organization that includes the central banks and financial regulators of major countries, at the request of G20 finance ministers and central bank governors. The TCFD recommendations encourage companies and others to disclose their governance, strategies, risk management, indicators and targets related to climate change-related risks and opportunities.
Under the common group slogan “Growing together with  ,” the Company aims to grow and develop together with stakeholders and at being a company that can contribute to society. Recognizing that climate change mitigation and adaptation are issues that need to be addressed now, we are working company-wide towards the reduction of CO2 emissions, including the greater efficiency of energy use and labor-savings.
,” the Company aims to grow and develop together with stakeholders and at being a company that can contribute to society. Recognizing that climate change mitigation and adaptation are issues that need to be addressed now, we are working company-wide towards the reduction of CO2 emissions, including the greater efficiency of energy use and labor-savings.
Governance and risk management
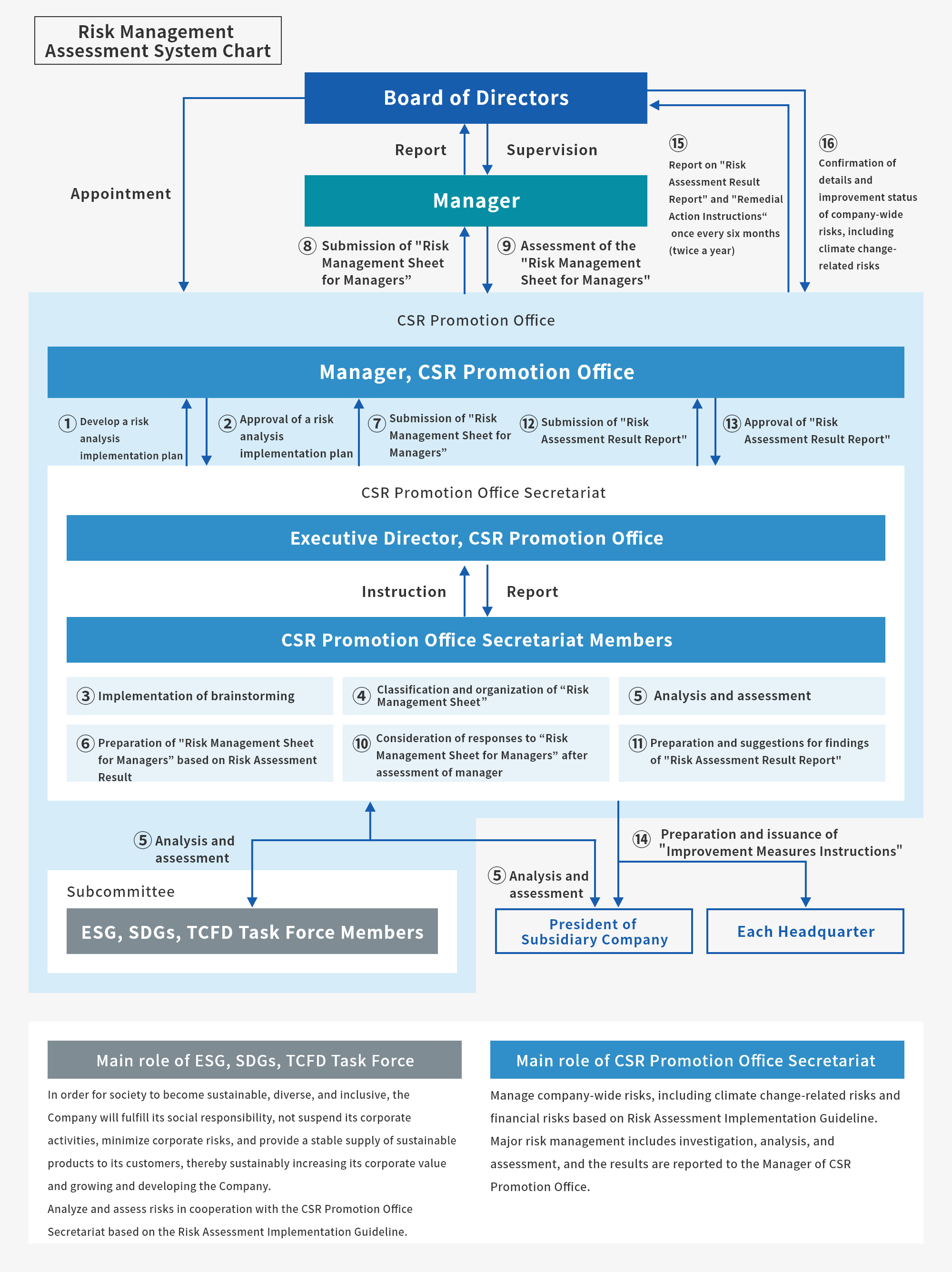
At the Company, managers are responsible for all risk management, and we have established a Compliance (CSR) Promotion Office. The authority to implement all risk management except assessments by managers has been delegated to CSR Promotion Office. CSR Promotion Office manages company-wide risks, including climate change-related risks, and financial risks in accordance with the Risk Management Regulations and the Risk Assessment Implementation Guideline, and managers assess them.
In addition, we have established an ESG, SDGs, TCFD Task Force as a subcommittee of CSR Promotion Office, and in cooperation with the CSR Promotion Office Secretariat, it identifies, assesses and manages comprehensively environmental and social risks, including climate change-related risks, based on the Risk Management Regulations and the Risk Assessment Implementation Guideline.
The matters discussed in CSR Promotion Office as well as the rates of achievement and state of progress of ESG, the SDGs and TCFD are reported to the Board of Director every six months (twice a year). And with these twice-yearly reports, the Board of Directors manages the progress of climate change-related risks and monitors the state of handling of risks that it has continuously identified.
Strategy
Under the TCFD recommendations, we classified climate change-related risks into the two categories of transition risks and physical risks, and considered risks based on the recommendations. In doing so, we identified major risk items assumed to be highly related to the Company’s business, assessed their impact based on the Risk Assessment Implementation Guideline, and organized our policies for handling as shown below. As the method for assessing the risks and opportunities related to climate change, we consider their relative importance to the Company and stakeholders taking factors such as trends in international society and the expectations of stakeholders into account, consider the time axis as short-term (one to two years), medium-term (three to five years) or long-term (six years or longer), assess the order of priority by performing 2030 scenario analysis qualitatively using a 1.5°C scenario and a 4°C scenario based on information from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and others, and assess their importance using the three levels of large, medium and small.
Transition risk
| Risks |
Details of risks |
Assessment of
importance |
Timing of
occurrence |
Policy for handling |
Policies
and
regulations |
Carbon tax and
price |
- The introduction of oil and coal taxes and carbon taxes, as well as the expansion of the emissions trading system, will progress. |
Medium |
Medium-term |
- Reduction of GHG emissions by installing solar power generation and introducing energy-saving equipment
- Suppression of fossil fuel consumption by introducing eco-cars
- Cost pass-through to product prices
|
Carbon emission
targets and policies/
of various countries |
- Total emissions regulations for GHG emissions will be strengthened and introduced. |
Small |
Medium-term |
Strengthening of
regulations on
products |
- The use of recycled materials in packaging and shipping containers will be made mandatory.
- Laws on container recycling will be strengthened.
- Monitoring of the traceability of sustainable products will be strengthened, and the decline of brand image and the spread of inappropriate information when incidents occur will hasten.
|
Small |
Medium-term |
- Improvement of the longevity of chemical solutions
- Greater efficiency of raw material use, including the introduction of electroless Ni recovery systems and the promotion of precious metal recovery and recycling
- Strengthening of recycling initiatives, including the adoption of chemical returnable containers for chemicals and the use of environmentally friendly products, packaging materials and equipment
|
Regulations on
water use |
- Water intake at production bases in areas of high water stress will be restricted and operations suspended. |
Medium |
Short-term |
- Greater efficiency of water use including internal wastewater management, the introduction of circulating water systems, the adoption of liquid raw materials and the introduction of automatic washing machines
- Purchasing of water
- Implementation of alternative production within the Group
|
Power supply
restrictions |
- Production volume will decrease due to power supply being limited. |
Small |
Short-term |
- Diversification of electric power, including the installation of solar power generation, the introduction of internal power generation facilities and the introduction of new electric power
- Greater efficiency of the use of external electric power by installing solar power generation and introducing energy-saving equipment
|
Industry
and market |
Changes in energy
prices |
- Energy costs will fluctuate due to soaring oil prices and renewable energy levies, failures with energy mix policies, and GHG emission regulations.
- Production and distribution processes will not become more efficient, and we will be at a disadvantage in competition with competitors.
- Energy efficiency will not advance and we will be impacted by increases in energy prices.
|
Small |
Medium-term |
- Greater efficiency of the use of external electric power, including installing solar power generation and introducing energy-saving equipment
- Suppression of fossil fuel consumption by introducing eco-cars
|
Soaring raw
material prices |
- The prices of major raw materials will rise due to weather, natural disasters, the supply and demand balance, etc.
- The shift to raw materials adapted to climate-change will not take place in time and it will be difficult to secure the required amounts of raw materials.
|
Large |
Long-term |
- Multiplication of suppliers
- Appropriate inventories considerate of the supply and demand balance and procurement costs
- Consideration of alternative raw materials
|
Changes in
customer behavior |
- Consumer preferences will change rapidly in association with climate change, and product development and public relations strategies will fall behind, leading to competitive disadvantage.
- Product demand will fluctuate due to changes in temperature associated with climate change.
- Momentum to consider the environment will increase and demand for products that do not contribute to the reduction of GHG emissions will decrease.
|
Medium |
Medium-term |
- Early grasping of customer orientations
- Promotion of product development that reflects customer orientations
|
| Technology |
Decarbonization of
energy sources |
- While GHG emissions are reduced due to reductions in the emission factor of grid power, on the other hand, electricity procurement cost will increase due to renewable energy levies.
- The transition to renewable energy will progress throughout society and increase the renewable energy ratio required will rise.
|
Small |
Medium-term |
- Greater efficiency of the use of external electric power, including installing solar power generation and introducing energy-saving equipment
|
| Reputation |
Reputation among
customers |
- The stance towards and results in initiatives aimed at climate change problems will more easily impact the evaluation of the Company by customers.
- Not disclosing appropriate information about climate change will lead to a decline in reputation.
|
Medium |
Medium-term |
- Early grasping of customer trends
- Promotion of product development that reflects customer orientations
- Positive information disclosure
- Promotion of dialogue with stakeholders
|
Reputation among
investors |
- The state of disclosure of non-financial information on climate change will be emphasized more, and the Company’s reputation among investors and financial institutions will fluctuate.
- The Company will be unable to issue green bonds tied to climate change measures (water-saving equipment, etc.) so fund procurement will become difficult.
|
Small |
Medium-term |
- Positive information disclosure
- Promotion of dialogue with stakeholders
|
Physical risk
| Risks |
Details of risks |
Assessment of
importance |
Timing of
occurrence |
Policy for handling |
| Chronic |
Rise in average
temperature |
- It will be necessary to change production sites and processes in response to climate change, and to consider alternative raw materials.
|
Small |
Medium-term |
- Multiplication of suppliers
- Greater efficiency of the use of external electric power, including installing solar power generation and introducing energy-saving equipment
|
Changes in water
supply and demand |
- Drought will intensify in areas around overseas production plants and they will be affected by rises in water and groundwater prices.
- Operating costs will increase due to water shortages in the supply chain.
|
Medium |
Short-term |
- Greater efficiency of water use including internal wastewater management, the introduction of circulating water systems, the adoption of liquid raw materials and the introduction of automatic washing machines
- Purchasing of water
- Implementation of alternative production within the Group
|
| Rise in sea levels |
- Storm surge damage will occur at production and distribution sites located on the coast.
|
Small |
Long-term |
- Multiplication of suppliers
- Promotion of BCP initiatives such as the installation of waterproofing embankments
|
| Acute |
Intensification of
abnormal weather |
- Serious wind and flood damage, the suspension of factory operations and logistics due to landslides, and losses due to property damage (owned facilities, equipment, etc.) and the disposal of goods will occur.
- Measures against wind and flood risks will be delayed, and the vulnerability of the supply chain due to heavy rain and typhoons will lead to competitive disadvantage.
|
Medium |
Long-term |
- Promotion of BCP initiatives such as the securing of emergency power and the installation of waterproofing embankments
- Implementation of alternative production within the Group
|
Assessment of business impact
We assess the business impact of risks that are significant and calculable. We have quantified the impact on business in the case of the 1.5°C scenario with regard to transition risk and in the case of the 4°C scenario with regard to physical risk.
| Risk |
Details of risk |
Impact (100 million yen) |
| Policies and regulations |
Carbon tax and price |
- The introduction of oil and coal taxes and carbon taxes, as well as the expansion of the emissions trading system, will progress.
|
1.22 |
| Regulations on water use
|
- Water intake at production bases in areas of high water stress will be restricted and operations suspended.
|
1.76 |
| Power supply restrictions |
- Production volume will decrease due to power supply being restricted.
|
0.58 |
| Industry and market |
Soaring raw material prices |
- The prices of major raw materials will rise due to weather, natural disasters, the supply and demand balance, etc.
- The switch to raw materials adapted to climate-change will not take place in time and securing the required amounts of raw materials will be difficult.
|
11.93 |
| Chronic |
Changes in water supply and demand |
- Drought will intensify in areas around overseas production plants and we will be affected by increased water and groundwater prices.
- Operating costs will increase due to water shortages in the supply chain.
|
1.76 |
| Acute |
Intensification of abnormal weather |
- The suspension of factory operations and logistics due to serious wind and flood damage, and landslides, and losses due to property damage (owned facilities, equipment, etc.) and the disposal of goods will occur.
- Measures against wind and flood risks will be delayed, and the vulnerability of the supply chain due to torrential rain and typhoons will lead to competitive disadvantage.
|
3.21 |
Chronic
In addition, with regard to the opportunities for the Company, we have also organized the impacts of those that are highly related to the Company’s business as shown below.
| Opportunities |
Details of opportunities |
Assessment of
importance |
Timing of
occurrence |
Greater efficiency
of resources |
Use of more efficient transportation methods |
- Energy-saving of transportation methods such as railways, ships and airports
|
Small |
Long-term |
| Efficient construction |
- Greater resource efficiency and improvement of productivity through the introduction of smart factories, eco-buildings, etc.
|
Small |
Long-term |
| Reduction of water use and consumption |
- Greater resource efficiency and improvement of productivity through the reduction of water use in manufacturing processes
- Water is purified at water purification plants using energy, but we contribute indirectly to reducing the amount of energy, etc.
|
Small |
Long-term |
| Energy sources |
Use of energy sources with low GHG
emissions |
- Introduction of renewable energy at Company-owned facilities (installation of solar power, etc.), strengthening of energy savings
|
Small |
Medium-term |
Products and
services |
Development and or expansion of
products and services with low-GHG
emissions |
- The development of products that contribute to energy saving, renewable energy, and energy creation will advance or demand will increase
|
Small |
Long-term |
Development of new products and
services through R&D and technological
innovation |
- We will research and develop new products and services that contribute to decarbonization.
- Technological development of systems for new fuels (hydrogen, etc.)
|
Small |
Long-term |
A shift in customer (consumer)
preferences |
- Needs will expand as customers come to favor products and services that contribute to decarbonization
|
Small |
Medium to
Long-term |
| Elasticity |
Participation in renewable energy
programs and adaptation of energy-
saving measures |
- Opportunities such as the development of new products, business expansion and the building of unique resource circulation models that will strengthen R&D capabilities and become climate countermeasures by responding to climate change
|
Small |
Medium-term |
Metrics and Targets
The Uyemura Group recognizes countermeasures against climate change as an important issue and is working on various initiatives for reducing CO2 emissions, such as energy efficiency and conservation (installation of solar power and adoption of energy-saving equipment).
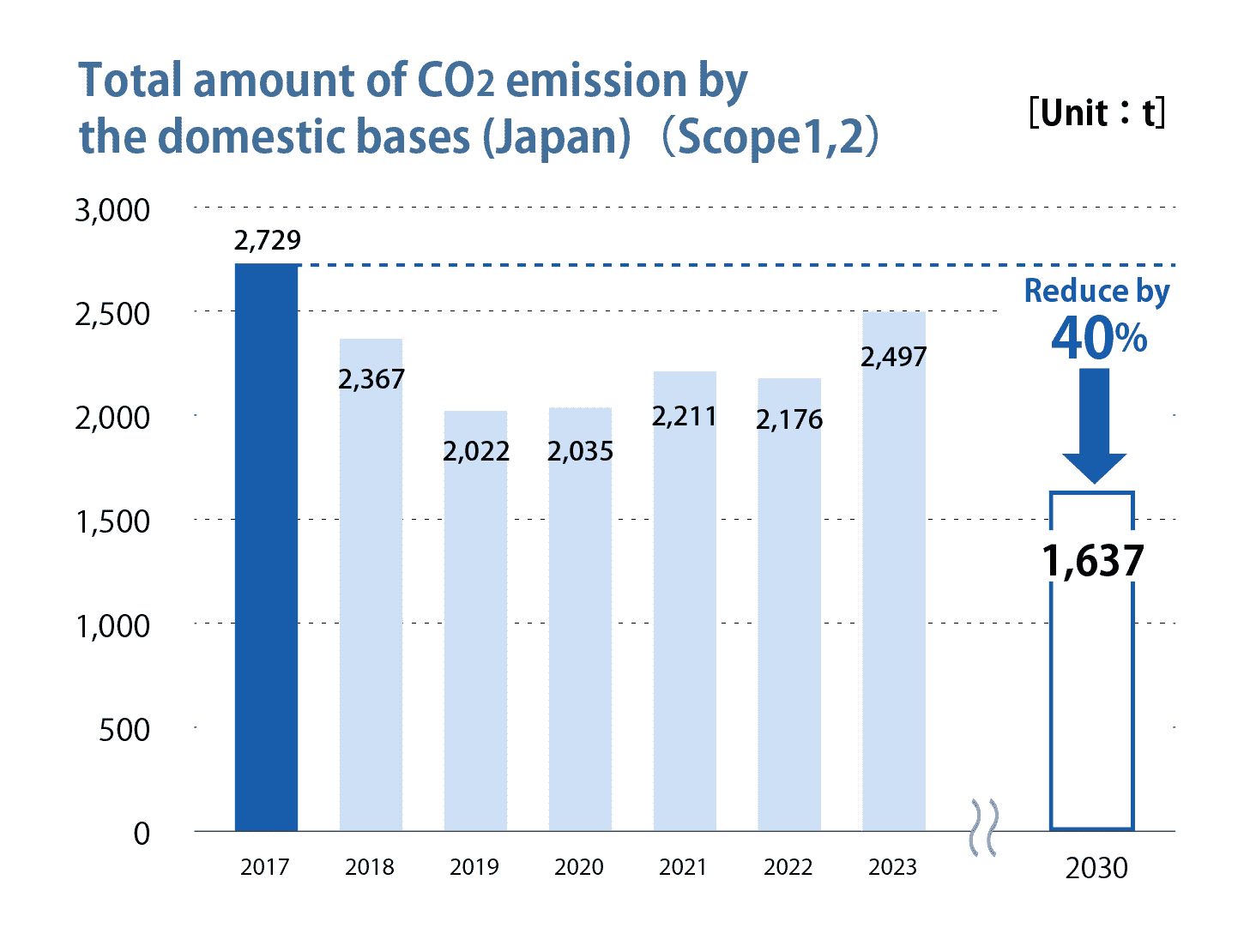
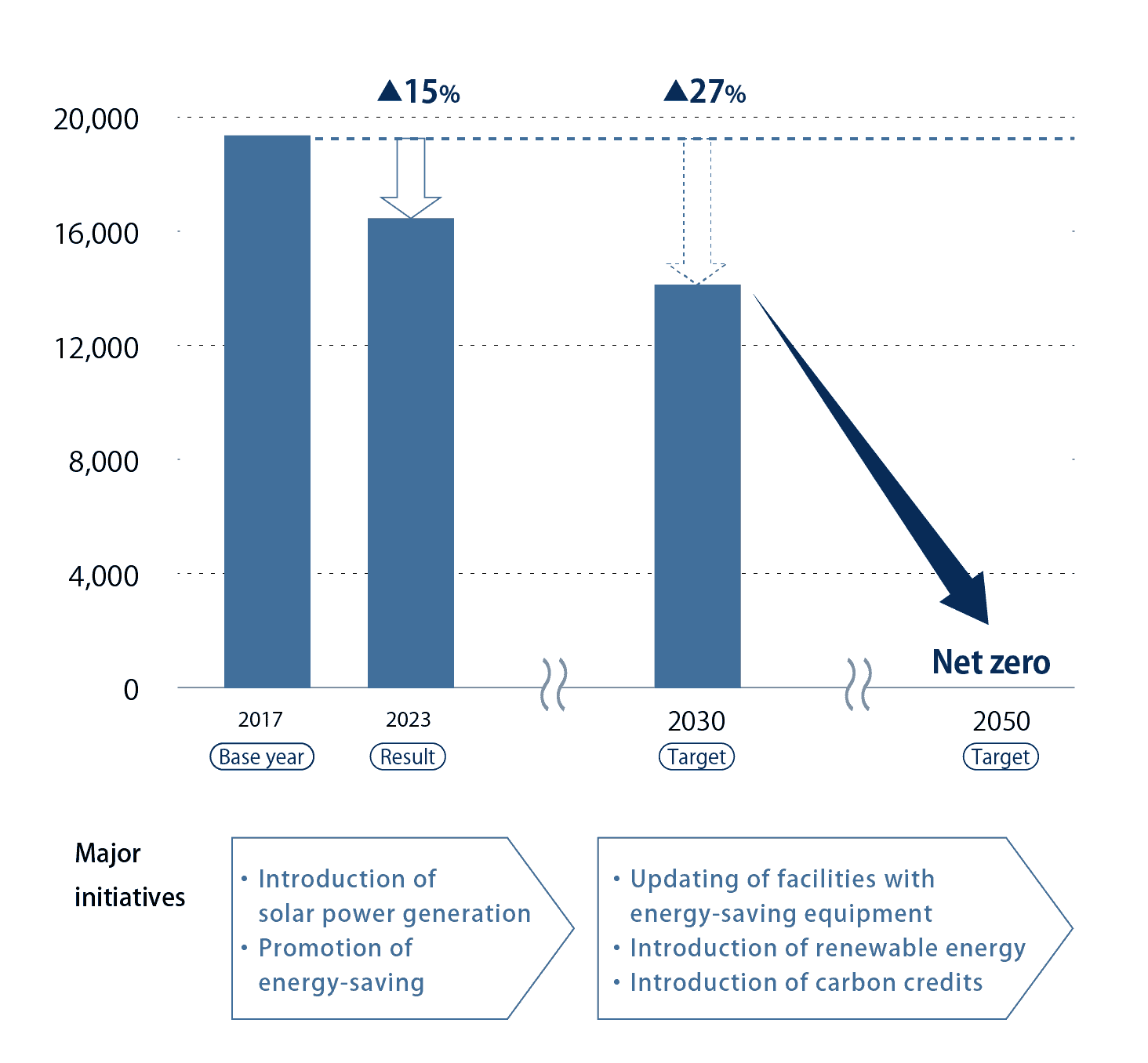
We have set "reduction of CO2 emissions" as one of our environmental goals and aim to reduce the Group’s CO2 emissions by 27% by 2030 (compared to 2017) with a 40% reduction in Japan and a 25% reduction overseas.
In addition, we will take on carbon neutrality (net zero emissions) by 2050 in order to realize a sustainable society.
CO2 emissions(Scope1,2)in 2023 and interim targets for 2030
| CO2 emissions(compared with 2017) |
CO2 emissions
(compared with 2017) |
Year 2023 |
2030 Interim target |
| Domestic bases (Japan) |
Reduction rate 9% |
Reduction rate 40% |
| Overseas group companies |
Reduction rate 16% |
Reduction rate 25% |
The path to carbon neutrality